A 2024 supply chain survey says that companies that adopt Inventory distribution strategies can reduce delivery time by almost 50% and decrease logistics expenses by 15 to 20%.
So, Inventory distribution plays a vital role in delivering to customers quickly and cost-effectively. Inventory distribution process involves the storage and distribution from the central warehouse to other warehouses or micro fulfillment centers located in various geographical regions. It does order fulfillment faster and ensures customer satisfaction, which is quite essential for the growth of the business.
What Is Inventory Distribution?

Inventory distribution is the distribution of inventories in multiple warehouses or fulfillment centers.
The manufacturer or supplier stores products in a centralized warehouse in a traditional inventory model. Here, the ordered product is picked, packaged and handed over to the shipper from the centralized warehouse. This delays the order fulfillment process and can dissatisfy customers.
However, in an inventory distribution or distributed inventory model, the inventories are distributed in warehouses of various geographical locations. When a customer orders, the warehouse and logistics staff prepare for the order fulfillment. It delivers the product faster to the customer and thus enhances customer satisfaction. The business has its fulfillment center or stores the product in the warehouses of a third-party logistics provider.
How Does Inventory Distribution Differ From Inventory Management Or Warehousing?

Inventory distribution focuses on distributing products in multiple warehouses or fulfillment centers.
Simple inventory management involves real-time tracking of stocks to prevent issues such as overstocking and out-of-stock problems.
Warehousing is a physical storage facility that stores products and manages inventory until a customer places an order. Now, most modern warehouses leverage advanced technology, such as a warehouse management system. It optimizes the warehouse layout and enhances the ecommerce fulfillment process.
Why Inventory Distribution Matters For Business?

1. Operational Efficiency
A distributed inventory model keeps inventory closer to the customer. This allows warehouse staff to pick, pack and ship faster to the customers. So inventory distribution does order fulfilment faster and increases customer satisfaction.
2. Reduces Shipping Costs
When the products are stored nearer to the customer, it reduces the business's shipping costs.
The businesses that transport boxes of tiles or wood pieces spend a lot of money on shipping, especially when delivering products over longer distances. However, when they use the inventory distribution model, they can see a remarkable decrease in shipping costs.
3. Customer Satisfaction
Today, most customers want their ordered products to be delivered within 1-2 days. Distribution inventory management keeps products closer to the customers and provides them more quickly. This increases brand reputation in the market and increases customer satisfaction.
4. Better Market Penetration
A distributed inventory model enables businesses to deliver products and services to multiple geographical areas. When a company keeps its stock in multiple regions, it can easily enter new markets and efficiently serve different customer bases.
Different Types Of Inventory Distribution Strategies
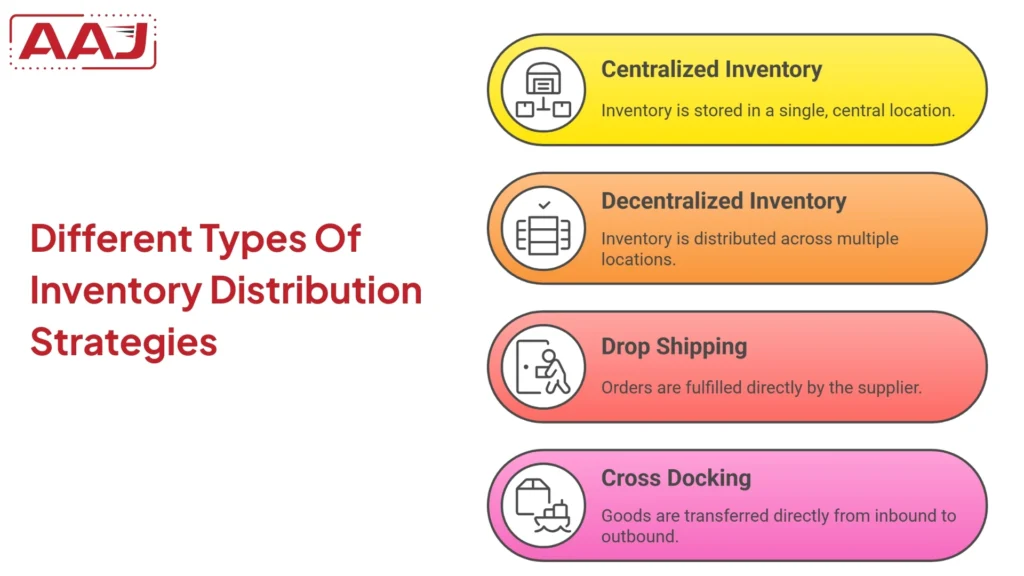
There are various types of inventory distribution strategies. Here is a list of them below.
1. Centralized Inventory Distribution
Centralized distribution is a strategy in which a company keeps all its goods and products in a single warehouse facility and ships products to all regions in India.
Pros
- Easy to manage and track inventories
- Reduces the risk of overstocking issues
- Business has to bear lower holding costs
Cons
- It takes a longer time to deliver products to the customer
- Businesses have to bear high transportation costs, especially for customers who live near a centralized warehouse
2 . Decentralized Inventory Distribution
Decentralized distribution is a strategy where a company keeps its goods or products in multiple warehouses or fulfillment centers in India.
Pros
- Lower shipping costs
- This type of strategy does order fulfillment faster and enhances customer satisfaction
Cons
- Higher holding costs
- It becomes difficult for the business to track inventories in all the warehouses
3. Drop Shipping
Drop shipping is a strategy where the manufacturer ships the products or services directly to the customer. Here, there is no need for the product storage in a warehouse.
Pros
- There is no need for storage facilities
- Businesses do not have to worry about inventory management
- Easy for a growing business
- Overhead expenses are pretty low for a business, as it has to purchase or store inventory
Cons
- It becomes difficult for the business to establish a strong brand identity because it lacks control over quality and packaging operations.
- There may be complexities with shipping operations.
4. Cross Docking
Cross-docking is an inventory distribution technique where the goods received from the inbound trucks are transferred directly to the outbound trucks. The products require little or almost no storage.
Today, most businesses utilize the cross-docking technique. They consolidate products from multiple suppliers and break them into smaller lots. The logistics company then organizes them properly to efficiently deliver to various retail stores, warehouses, or fulfillment centers. This technique requires loose coordination with suppliers and freight carriers.
Pros
- This technique does order fulfillment faster.
- Minimal inventory holding costs.
Cons
- It requires precise coordination between suppliers and carriers, which is not always possible.
Key Factors To Consider In Inventory Distribution Planning
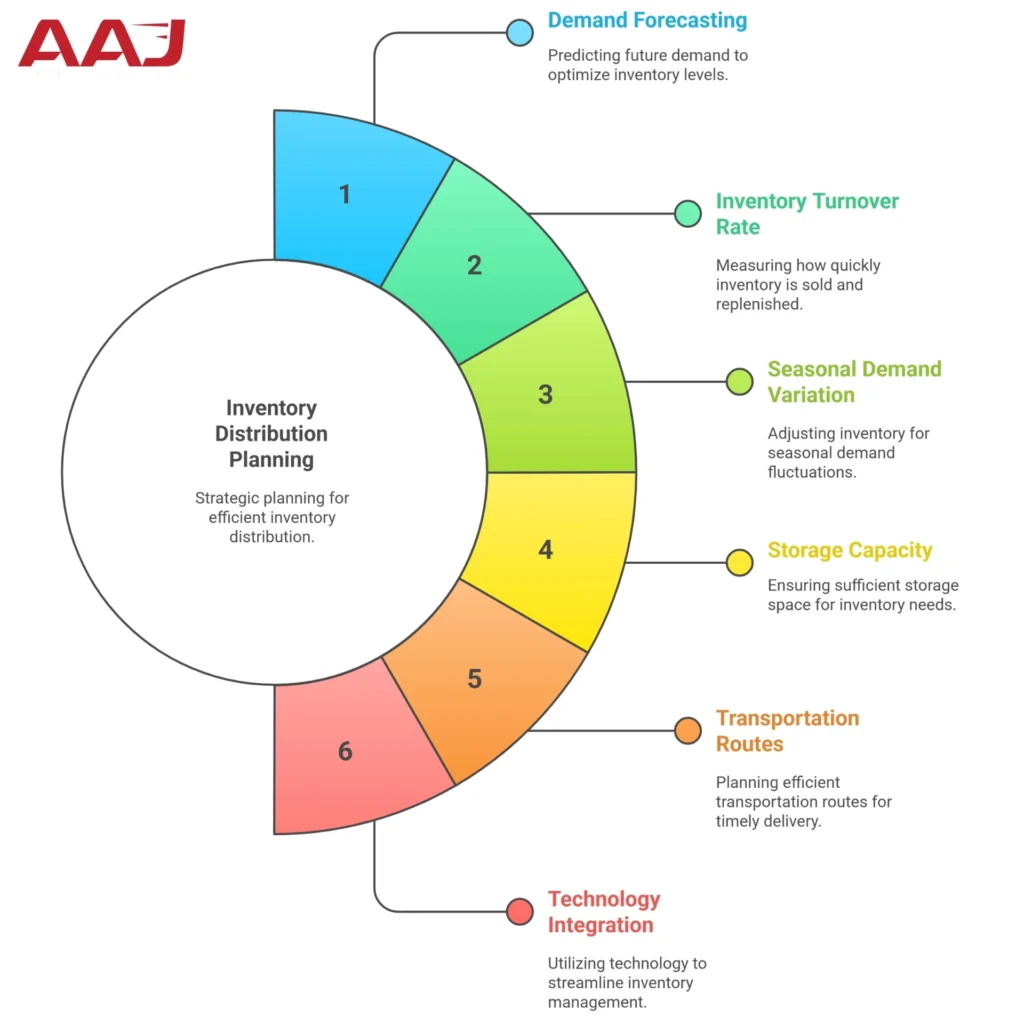
Inventory distribution planning depends on various factors. Here is a list of them below.
1. Demand Forecasting
It involves forecasting product demand based on market trends and historical sales data. Accurate demand forecasting helps a business position inventories in the correct warehouse location or fulfillment center. It even helps to avoid overstocking and understocking issues in a particular warehouse.
2. Inventory Turnover Rate
It involves the rate at which inventories are sold and replaced in the warehouse over a specific period. A business can calculate Inventory Turnover by dividing the cost of goods sold by the average inventory for a particular period. A high inventory turnover rate indicates that goods or products are sold faster, while a weak rate suggests weak sales and excess inventory stored in the warehouse.
A business can store products with a high turnover rate in areas with high demand. It can store slow-moving goods in the central warehouse.
3. Seasonal Demand Variation
There can be fluctuations in product demand based on season or festival. For instance, the demand for air conditioning increases in the summer season, and there can be an increase in demand for heaters during the winter season in India. A business needs to adjust the inventory distribution in the warehouse and fulfillment center based on the previously seasonal demand data.
4. Storage Capacity
Storage capacity indicates the amount of space available in the warehouse for storing goods and products. Businesses must store the products efficiently and in properly designated locations to avoid congestion. The staff can easily pick the ordered product from the shelves or racks of the warehouse.
5. Transportation Routes
The business can ship products to customers through various transportation routes, such as air, rail, road, or sea. However, the transport company in India should choose an efficient transportation route to reduce shipping costs and deliver faster to customers.
6. Technology Integration
Businesses should utilize advanced technology, such as a warehouse management system, AI, and enterprise resource planning, for real-time tracking of inventories, optimizing warehouse layout, and making order fulfilment faster. It increases brand reputation in the market and enhances customer satisfaction.
Best Practices To Improve Inventory Distribution Efficiency

Businesses can utilize advanced technologies to improve inventory distribution efficiency.
1. Real-Time Tracking
Businesses can use RFID, barcode scanning and cloud-based systems to track inventories in all the warehouses and distribution centers. It can keep stock accordingly in various storage locations. Usage of these advanced systems can prevent overstocking and out-of-stock issues.
2. Optimize Warehouse Locations
When a business places the products in warehouses or fulfillment centers closer to customers, it can deliver orders faster. Again, it will reduce the business's transportation costs.
3. Implement Demand Driven Replenishment
The business should forecast product demand, observe market trends, and keep stock accordingly. It allows the Company to maintain enough inventory in the demanding locations to avoid out-of-stock issues.
4. Automate Repetitive Tasks
Businesses can adopt technology, such as warehouse and inventory management systems, AI, and robotics, to automate repetitive tasks like picking ordered products, transporting products from one place to another, and generating reports. Automation can speed up various operations inside the warehouse and reduce human error.
Common Mistakes In Inventory and Stock Distribution
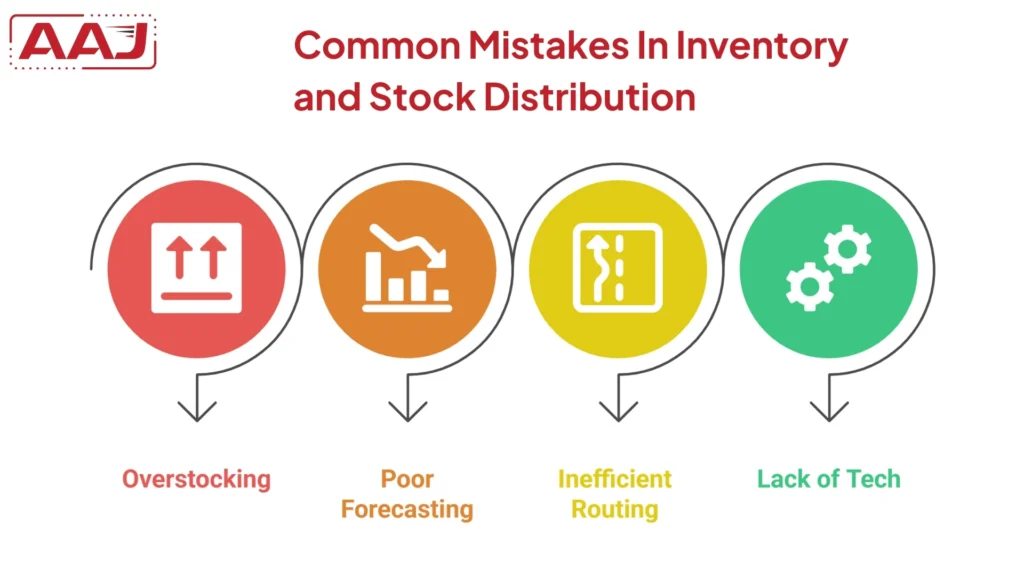
When a business plans for inventory and stock distribution, it faces a few challenges. Here is a list of them below.
1. Overstocking Leading To High Carrying Costs
If a business stores excess inventory in multiple warehouses, it can raise overstocking issues and holding costs. Again, some products can get damaged over time.
Solutions: Businesses can adopt demand forecasting tools or advanced technology to maintain optimal stock levels in each warehouse.
2. Poor Demand Forecasting
Inaccurate forecast demand can lead to overstocking problems in lower-demanding areas and out-of-stock issues in highly demanding areas.
Solutions: Businesses should use market trends, seasonal data, and AI-based forecasting tools to predict product demand.
3. Inefficient Routing
Inefficient routing can raise transportation costs and cause delays in delivering products to customers.
Solutions: Businesses should utilize a transport management system to choose an efficient route for goods delivery.
4. Lack Of Tech Adoption
When a business does not utilize advanced software, inventory visibility inside the warehouse is reduced. Errors in tracking or picking products can cause delays in the fulfilment process of orders.
Solutions: Businesses should integrate a warehouse management system and enterprise resource planning to improve product visibility and automate various processes inside the warehouse.
Future Trends In Inventory Distribution
- Utilizing AI and machine learning to forecast product demand and analyze sales patterns.
- Have to keep their products in automated micro fulfillment centers and fulfil customer demands.
- Businesses will utilize conveyor systems, robotics, and autonomous mobile robots to process orders faster.
- Companies will utilize blockchain technology to track product movement.
- Have to adopt electric vehicles to transport goods to customers.
Final Words
A study says 73% of customers remain loyal to a brand if it delivers faster and reliably. Companies that adopt inventory distribution strategies fulfill customer orders faster. However, they can optimize the inventory distribution strategy by adopting advanced technology, such as AI, machine learning, and software like a warehouse management system.
;;;;;



