Warehouse putaway is the process that determines where inventory is stored after it is received and how efficiently it can be picked, replenished, and counted later. While most warehouses treat putaway as a routine movement task, the way inventory is assigned to storage locations directly impacts space utilization, picking speed, and labour efficiency.
This guide explains what putaway in warehouse operations entails, how the putaway process works in real-world environments, and how warehouse management systems influence putaway decisions. You’ll also learn why common putaway methods fail, how to choose the right approach based on SKU behaviour and layout, and what changes deliver the biggest operational gains without disrupting daily operations.
What Is Warehouse Putaway?
Warehouse putaway is the process of assigning incoming inventory to the right storage locations after receiving. It directly affects picking speed, space utilization, inventory accuracy, and order fulfillment performance. This process is essential to maintaining a well-stocked, easily accessible inventory.
Proper putaway in warehouse management optimizes space and reduces the time required to pick ordered products. Thus, it improves the order fulfillment speed and enhances customer satisfaction.
Why Warehouse Putaway Matters More Than Most Teams Realize
Warehouse putaway is the first strategic decision made after the products enter the warehouse. It affects all the important operations in the warehouse for the following reasons.
1. Picking Speed And Efficiency
Proper warehouse putaway improves order picking operations. For example, if the warehouse staff keeps fast-moving products in the nearest picking zones, it will pick faster, improving overall order fulfilment speed.
2. Impacts Inventory Accuracy
Proper warehouse putaway ensures that physical stock matches the stock updated in the system. It improves inventory accuracy in a warehouse.
3. Optimises Space In The Warehouse
Smart warehouse putaway optimizes space and even prevents overstocking and understocking.
What Actually Happens During A Putaway Process In The Warehouse?
1. Receiving
The seller sends the goods to the warehouse, where they are further unloaded at the receiving dock. The warehouse staff then notes basic details such as the supplier's name, the PO number, and more.
Delays can occur when there are fewer unloading staff in the warehouse. Dock congestion can also contribute to delays in receiving goods.
2. Verification
The warehouse staff verifies the product received at the receiving dock. The staff checks the quantity and ensures that it is as per the order. Simultaneously, the staff verifies its quality and ensures none are damaged.
If the warehouse relies entirely on manual processes, it can delay product verification.
3. Assignment
A warehouse can rely entirely on manual processes for storing received products. The supervisor assigns storage locations based on product size and market demand. Some warehouses use advanced software, such as a warehouse management system, to allocate products to their designated locations.
Assigning storage locations can get delayed if the warehouse is already congested.
4. Movement
Now, the warehouse staff transports goods from the receiving area to the storage locations. The staff can use forklifts or pallet jacks to transport products. Delays can occur if the receiving dock is far from the storage locations.
5. Confirmation
The warehouse staff conducts final confirmation and ensures that the goods are in their assigned location. The staff scans both the product and the storage location barcodes using a handheld device. The device connects to advanced software, such as a warehouse management system. The system automatically updates inventory in real time when warehouse staff scan the product and its storage location.
Explaining Physical Putaway and System Putaway
Physical Putaway
Physical warehouse putaway begins when inventory is unloaded at the receiving dock. Here, the warehouse staff transport goods to designated locations, such as shelves or racks, depending on the product's nature. Sometimes workers use equipment like forklifts or pallet jacks to transport products to their designated locations. However, physical warehouse putaway depends heavily on manual effort. It increases the business's labour costs. Again, errors in placing goods on the racks or bins can reduce picking efficiency. Physical putaway is still commonly used in small warehouses with limited SKUs or stable inventory flow, where software-driven optimization may not be cost-effective.
System Putaway
System warehouse putaway does not depend heavily on warehouse staff. The warehouse uses advanced software, such as a warehouse management system, to assign locations to goods received from the seller. The software assigns the storage location based on the product type, size, turnover rate, and storage zone. It ensures that the products are stored inside the warehouse in efficient locations. System warehouse putaway improves inventory accuracy and order picking speed compared to physical putaway.
Different Types of Warehouse Putaway Methods
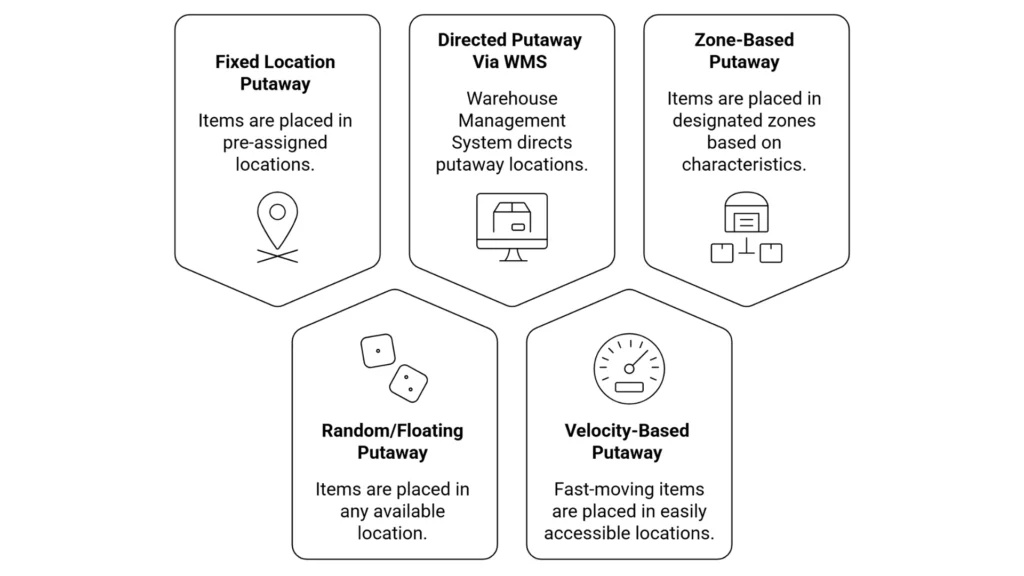
There are almost 4 types of warehouse putaway methods. They are in the list below.
1. Fixed Location Putaway
Here, each product or good has a permanent storage location, i.e., in racks or bins. Every time the warehouse staff receives the product, it is stored in the same location.
Fixed-location warehouse putaway offers various benefits; it enables faster picking because workers are familiar with the storage locations. There is less dependency on advanced software. However, this method works best for warehouses with stable SKU volumes and predictable demand, but becomes inefficient as inventory variety and scale increase.
2. Random/Floating Putaway
Here, the staff places the products in available empty spaces on the racks or shelves inside the warehouse. Advanced software, such as a WMS, identifies the empty location, and staff move the goods or products accordingly. Random or floating warehouse putaway works best for e-commerce and fast-moving consumer goods. This method optimizes the warehouse space but is 100 per cent dependent on advanced software.
3. Directed Putaway Via WMS
Here, advanced software, such as a warehouse management system, determines the most suitable location for storing received inventory. The WMS considers the product's size and weight, analyzes the storage conditions, and then determines the required storage space. This method works best for medium to large warehouses. It improves space utilization inside the warehouse storage facility and improves picking efficiency.
4. Velocity-Based Putaway
In a velocity-based warehouse putaway, the warehouse staff classifies the inventories based on the demand in the market, like fast-moving, medium-moving, and slow-moving. The staff places fast-moving products closer to the picking or dispatch areas. Again, the staff places the medium movers in mid-distance locations and the slow movers in higher racks. This method reduces picker time and improves the business's order fulfillment speed.
5. Zone-Based Putaway
Zone-based putaway divides the warehouse into various zones, such as fast-pick, hazardous, and temperature-controlled areas. The staff store the product according to their storage requirements, which improves safety in the shared warehouse.
If a warehouse has multiple zones, proper coordination among the team is required to avoid delays in product dispatch.
Put Away In Warehouse Management System - What The Software Decides Vs What Humans Still Control
WMS determines the putaway storage location based on the product's size and weight. It even tracks inventories in real time.
However, humans need to move products from one place to another by themselves or with forklifts or pallet jacks.
Common Putaway Mistakes That Reduce Picking Speed And Space Utilization
- If warehouse staff keep highly demanded items deep in the warehouse, it reduces picking efficiency. It even increases the business's order processing time and labour costs.
- Fixed bins remain half-empty when warehouse stock levels are low.
- If the zones inside the warehouse lack proper markings, staff store the product in the wrong location. It reduces layout efficiency and increases workers' travel time.
Common Putaway Mistakes That Slow Picking & Waste Space
Even well-run warehouses often struggle with putaway issues that quietly reduce picking speed and waste valuable storage space. Most of these problems start at the receiving stage and compound over time.
Placing fast-moving SKUs deep inside the warehouse
When high-velocity items are stored far from picking or dispatch zones, pickers spend more time walking than picking. This increases order turnaround time and labour costs, especially during peak periods.
Relying on fixed locations despite fluctuating inventory levels
Fixed bins often remain half-empty when stock levels drop. As SKU count increases, this leads to poor space utilization and artificial congestion, even when the warehouse has available capacity.
Manual putaway without system validation
Warehouses that rely only on manual location assignment often face inventory mismatches. A product placed in the wrong bin may remain “lost” in the system, leading to delays, stock adjustments, and emergency picking.
Poorly defined zones and location labels
Unclear zone markings, missing bin labels, or inconsistent rack numbering confuse warehouse staff. This increases travel time, causes misplacement, and slows down both putaway and picking activities.
Ignoring SKU size, weight, and handling requirements
Storing heavy or bulky items in hard-to-reach locations creates safety risks and slows movement. Similarly, mixing incompatible SKUs in the same zone increases handling errors.
Not updating the system for blocked or damaged locations
When damaged racks, blocked aisles, or temporary storage areas are not reflected in the WMS, the system continues assigning inventory to unusable locations, causing repeated exceptions.
Avoiding these mistakes helps warehouses improve picking efficiency, maintain accurate inventory records, and make better use of available storage space without expanding the facility.
How To Improve Putaway Without Redesigning The Entire Warehouse?
- The warehouse staff must scan barcodes for both products and storage locations.
- The bin, rack, and floor locations should be properly mapped in advanced software such as a WMS.
- The warehouse staff should regularly update the WMS to reflect blocked spaces or damaged products.
Warehouse Putaway vs Storage vs Picking
Putaway, storage, and picking are often used interchangeably in warehouse operations, but each serves a distinct purpose within the inventory flow. Understanding the difference is essential for optimizing warehouse performance.
Warehouse Putaway
Putaway is the process of assigning and moving incoming inventory to the correct storage locations after receiving and verification. It determines where products are stored and directly impacts how quickly they can be picked later.
Storage
It refers to holding inventory in designated locations until it is required for order fulfillment. Storage focuses on space management and product safety, but it does not involve decision-making about movement or order flow.
Picking
Picking is the process of retrieving items from storage locations to fulfill customer orders. It's speed and accuracy depend heavily on how well the putaway was executed earlier.
In simple terms, putaway sets the foundation, storage maintains inventory, and picking executes orders. Weak putaway decisions often lead to slow picking and inefficient storage, even when other warehouse processes are well-designed.
Final Words
Warehouse putaway is one of the most vital activities involved in warehouse management. It involves all activities from receiving goods from the seller to storing them at the storage location. Proper warehouse putaway improves safety and picking efficiency. It even maximizes the available space inside the warehouse and improves order fulfillment speed. A business can optimize warehouse putaway by using warehouse automation and advanced software, such as a warehouse management system.





