Order volumes are rising year in and year out in various warehouses and fulfillment centers. Again, customers want to receive their ordered products within one or two days. So many small- and medium-sized enterprises face challenges maintaining such high order volumes and delivering ordered products to customers as quickly as possible. Zone picking is one of the best ways to handle high-volume orders and improve order fulfillment.
What Is Zone Picking?
Zone picking is a warehouse management strategy that optimizes order fulfillment for an e-commerce business. Here, the warehouse facility is divided into multiple zones. Each zone has different product categories. There will be different workers in each zone. They need to pick only the ordered products from their assigned zones and bring them to the consolidated area for packaging and dispatch. So, zone picking reduces travel time and congestion inside the warehouse.
How Zone Picking Differs From Wave Picking, Batch Picking, And Cluster Picking?
| Features | Zone Picking | Wave picking | Batch picking | Cluster picking |
| Working | Here, the entire warehouse has various zones or distinct areas. The picker needs to collect the ordered products from the assigned zones. | Here a picker picks items of multiple customers in a single trip through the warehouse. | Here, a picker picks items for multiple customers in a single trip through the warehouse. | Here a single picker picks items for multiple customers at the same time using various totes,slots or bins. |
| Order Handling | Here, the WMS splits the order into various zones. | The WMS groups the order based on shipping deadlines or carrier schedules. | The warehouse staff pick multiple orders at a time. | The staff picks multiple orders at a time using multiple bins or totes. |
| Picker Movement | Minimal movement of picker. | The picker moves across the entire warehouse only when necessary. | The picker moves throughout the warehouse. | The picker moves across the entire warehouse. |
| Advantages | Less travel time | Strong schedule control | Efficient for similar orders | Picks multiple orders efficiently. |
How Zone Picking Works In A Warehouse?
1. Divide Warehouse Into Defined Zones
The warehouse has numerous zones based on produce size or weight, or on temperature-sensitive products. For example, a warehouse can have one zone for fresh products and another for frozen items. Similarly, another warehouse can have one zone for items that require a forklift for loading and unloading, and another zone can have hand-picked products.
2. Assigning Pickers To Specific Zones
The WMS assigns each picker to a specific zone. The picker is responsible for retrieving items only from that particular zone. So, here the picker does not roam around the entire warehouse to pick ordered products for various customers. This reduces workers' travel time and enhances a business's order fulfillment operation.
3. Orders Move Through Each Zone
Most warehouses use a sequential zone-picking method to fulfill orders. Here, each picker will pick the ordered products from their assigned zones, add them to the cart, and pass them to the next zone. The picker for the second zone collected all the ordered products from its zone, put them in the cart, and sent them to the next zone. Finally, all the products are collected from their respective zones, and the cart is moved to the consolidation area or delivery zone for packaging.
4. Consolidation and Sorting For Packing
Pickers from various zones collect all ordered products and bring them to the consolidation station. There are usually two ways of consolidating products, i.e, manual and automation. Manual consolidation is quite a time-consuming process and may involve errors. Here, the staff scans each product and groups them based on their order. But automated consolidations are pretty fast and have almost no errors. Conveyor systems or robotic arms consolidate the products automatically. The products finally move to the packaging station and get ready for dispatch.
Different Types Of Zone Picking
There are three types of zone picking. They are in the list below.
1. Sequential Zone Picking
Here, the picker picks products from one zone and passes them to the next zone. Let's discuss with an example. A picker picks products like pasta and tomatoes from one zone, puts them in the cart, then moves to the next zone. Another picker will pick the product, like cat food, from the zone, put it in the cart, and finally pass it to the next zone. This process gets repeated, and finally, the cart moves to the consolidation area.
2. Simultaneous Zone Picking
Simultaneous zone picking is a method in which each picker will produce from their specific zone. But here, the picker will not put them in the cart and set them aside for the next zone. Each picker will produce from the assigned zone at the same time and finally move to the consolidated area for sorting, packaging, and dispatching. This method is best suited for e-commerce fulfillment centers and warehouses with many zones.
3. Pick To Belt Zone Picking
Pick-to-belt zone picking is a method in which each picker picks ordered products from specific zones and places them on conveyor belts. The belt will automatically move all ordered products to the consolidated station. The products are further sorted and finally packed for dispatch. This method allows continuous picking without waiting for totes. Pick-to-belt zone picking is best suited for large warehouses or high-volume ecommerce operations.
Technologies That Improve Zone Picking Efficiency
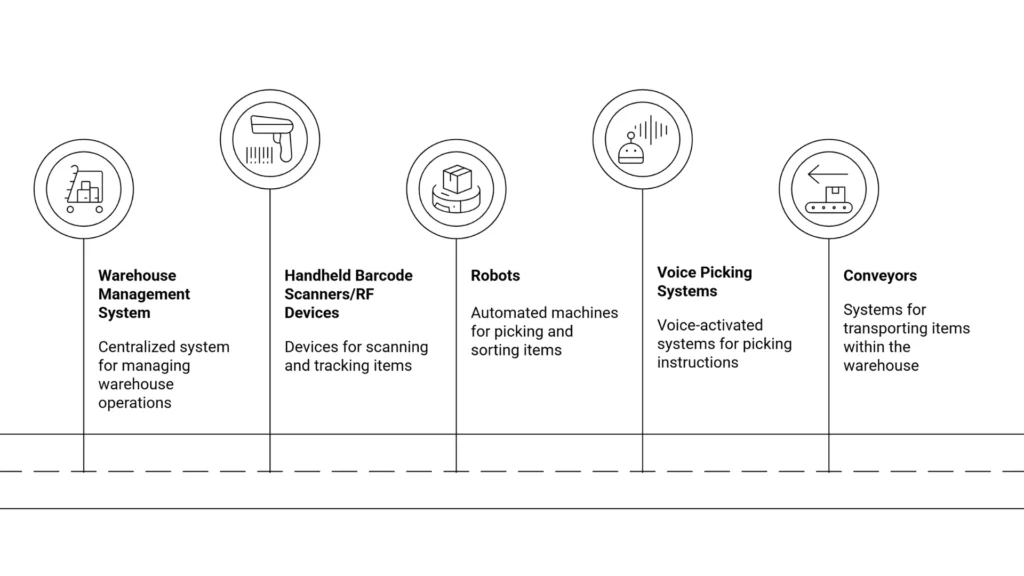
There are various technologies that a warehouse service provider can utilize to improve zone picking efficiency.
1. Warehouse Management System
This advanced software optimizes the warehouse layout and assigns zone-based tasks to each picker. The software can even track stocks in real time.
2. Handheld barcode Scanners/RF Devices
Handheld barcode scanners and RF devices help pickers to scan item barcodes. These portable tools connect to advanced software, such as a warehouse management system, and guide pickers through each step of the zone picking process.
3. Robots
Robots transport totes from one zone to another and reduce the travel time of workers in the warehouse.
4. Voice Picking Systems
Here, the picker receives instructions regarding the ordered product through a headset.
5. Conveyors
It automatically moves the product from zones to consolidation systems.
Benefits Of Zone Picking For Warehouses And E-commerce Operations
There are various benefits of zone picking for warehouses and e-commerce operations. They are in the list below.
- Higher Picking Speed: Here, each picker focuses on a small and well-defined area. It reduces travel time and boosts picking speed in a warehouse.
- Better Inventory Accuracy And Fewer Errors: Pickers become familiar with their assigned zones, which leads to fewer errors when picking ordered products. Pickers can use scanners or handheld barcode scanners to pick ordered products accurately.
- Scalability During Seasonal Picks: Zone picking makes it easier to handle seasonal products in the market, especially during festivals, holidays, or peak seasons. A warehouse company can add temporary staff to busy zones without disrupting the entire workflow.
- Lowers Labor Cost And Training Time: Zone picking reduces labor costs and training time because workers focus on a smaller area rather than the entire warehouse.
- Improves Throughput And Order Consolidation: Zone picking allows more orders to be picked and packed simultaneously. This improves the warehouse's order fulfillment efficiency and enhances customer satisfaction.
Challenges Of Zone Picking And How To Solve Them
There are a few challenges of zone picking, which are listed below.
1. Bottlenecks at Consolidated Area
Zone picking involves multiple zones. The pickers pick products across various zones and bring the ordered products to the consolidated table at the same time. When ordered products pile one after the other, it becomes challenging to sort and package products. Warehouse providers can use conveyor systems to speed up the process.
2. High Initial Setup Costs
Setting up zones, conveyors, and advanced technologies requires a higher initial investment. A 3PL service provider can use cost-effective tools, such as handheld scanners, before moving to automated processes.
3. Training Requirements For Accurate Picking
Zone picking requires training workers to pick products accurately. They need to understand the zone layout and how devices like scanners work.
Best Practices For Successful Zone Picking Implementation
There are a few practices that a warehouse provider can implement for successful zone implementation.
- Zones should have a simple and logical layout.
- Warehouse providers should use technology based on product volume. If a warehouse has a high volume of products, it should use advanced technology, such as conveyors, to speed up the order fulfillment process.
- A warehouse provider should optimize the consolidated area so that there will be enough space for sorting.
- A warehouse provider should first start with manual zone picking and then move to automation, like conveyors, to increase throughput.
Conclusion
Zone is an excellent warehouse strategy that optimizes the order picking process and enhances the order fulfillment process. It even reduces workers' travel time. Zone picking makes it even easier to pick and handle products during peak season or holidays. But it has a few limitations: setting up automated systems, such as conveyors, or using advanced technology, such as a warehouse management system, can be costly for small- and medium-scale enterprises.





