Research says the Indian e-commerce market is expected to reach US$163 billion by 2026. This explains the booming growth of e-commerce Companies in India. These companies will require a warehouse to store their inventory. Small and medium-sized companies often lack the funds to build their own warehouses and store products. They can keep their inventories in the managed warehouse. A third-party logistics provider manages these warehouses and handles various order fulfillment processes, including picking, packing, and shipping.
What Is A Managed Warehouse?
A managed warehouse is a type of warehouse where all operations are managed by a third-party logistics provider on behalf of the business. Most managed warehouses leverage technology, such as warehouse management systems. It optimises the entire warehouse layout and enhances the order fulfilment process.
The staff of the managed warehouse handles various warehousing operations like picking ordered products, packaging them, and finally handing them to the shipper. The shipper delivers the product to the customer's doorstep.
Key Characteristics Of Managed Warehouse
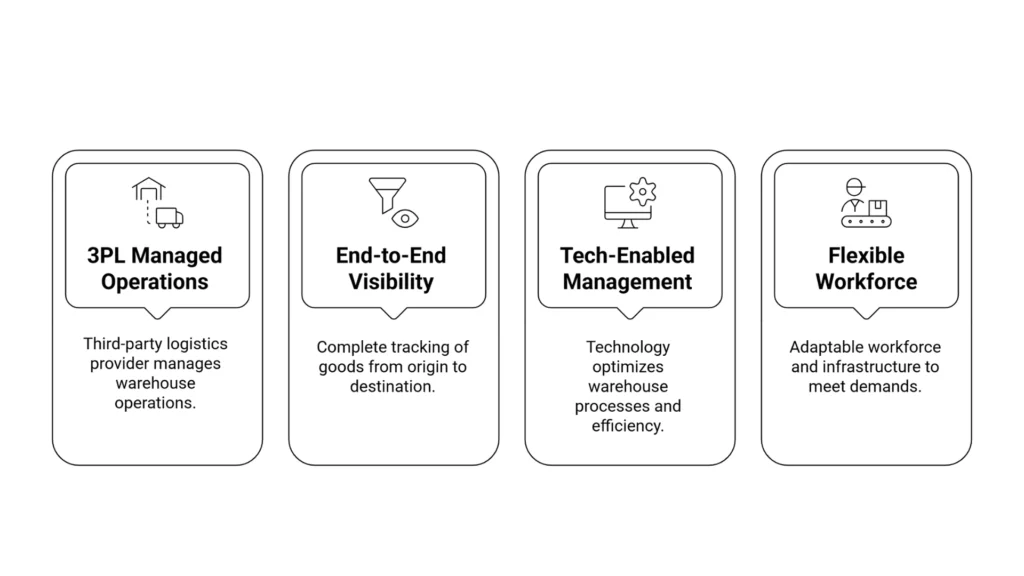
The characteristics of a managed warehouse are as follows.
1. 3PL Managed Operations
The staff of the managed warehouse handles various aspects of the order fulfillment process, like storage, picking, packaging, and shipping. A business does not have to worry about managing staff, purchasing equipment, or monitoring 3PL operations.
2. End-to-End Visibility
A managed warehouse leverages advanced technology, such as an inventory management system. The software tracks inventories in real-time and provides updates on them. This helps avoid the problems of overstocking and out-of-stock issues in a business. The updated stock data even helps businesses forecast product demand in the near future and make informed decisions accordingly.
3. Tech-Enabled Management
Managed warehouse leverage with advanced technology like a warehouse management system and automation. The warehouse management system optimizes storage and layout, and processes orders more efficiently. Automation tools, such as barcode scanning and robotics, speed up logistic operations and reduce manual errors.
4. Flexible Workforce And Infrastructure
Managed warehouses are highly flexible. The warehouse can scale up and down based on the product demand in the market.
There can be order spikes, particularly in certain seasons or holidays. A managed warehouse can be handled without hiring additional staff or renting extra space.
How Does A Managed Warehouse Work?
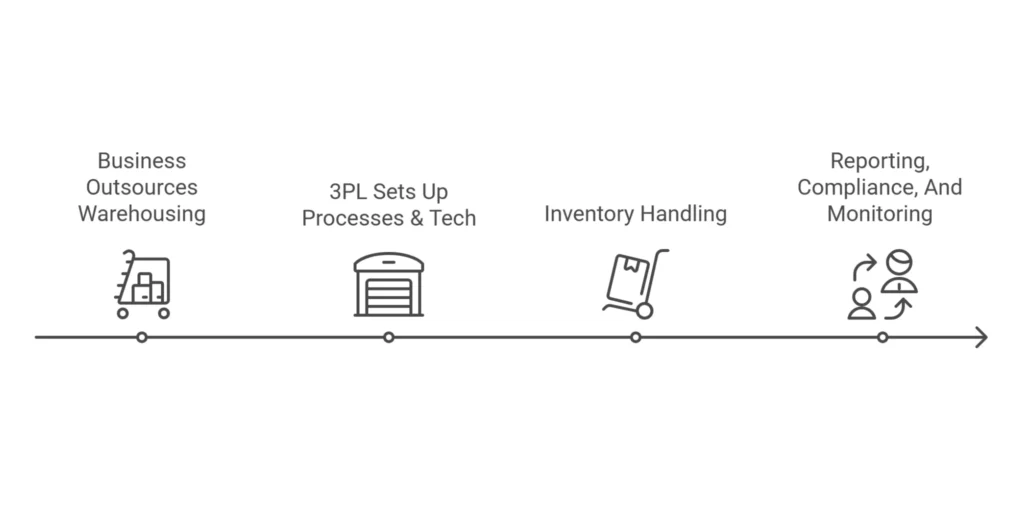
Here is a step-by-step guide on how a managed warehouse works.
1. Business Outsources Warehousing To A 3PL Service Provider
A start-up business typically has limited products for storage. It can store products in the store or in the office. However, as the company grows, managing inventory and shipping many products on time requires a significant amount of time and effort. A slight delay in delivering the order can negatively impact the brand. There comes the importance of a managed warehouse. The business can store products in such a warehouse.
2. 3PL Sets Up Processes & Tech
Most reputable managed warehouses utilize advanced technologies, such as warehouse management systems and automation. They even integrate with the existing platforms of their clients' businesses, such as enterprise resource planning and e-commerce websites.
3. Inventory Receiving, Storage, Picking, Packing, And Shipping Handled
The staff of the managed warehouse receives the inventories from the business. They inspect it thoroughly and ensure the product remains undamaged over time. When a customer orders products from the e-commerce website, the order details are sent automatically to the warehouse. The staff picks up the ordered product and thoroughly packs it to prevent damage during transportation. The staff then hand over the packaged product to the shipping company.
4. Reporting, Compliance, And Performance Monitoring Included
The managed warehouse continuously monitors the stored inventory and adheres to all safety standards. A business will receive detailed reports and updates about the stock availability for complete visibility.
Managed Warehouse VS Traditional Warehouse
| Features | Managed Warehouse | Traditional Warehouse |
| Operation | A 3PL service provider operates a managed warehouse. | A business owns a traditional warehouse and manages all the operations. |
| Investment. | There is no need for high capital investment for storing products in a managed warehouse. | A business needs to invest high capital for purchasing land, building a warehouse, managing staff ,and buying equipment. |
| Technology | Most of the managed warehouses use advanced technology like a warehouse management system to speed up the order fulfillment process. | A traditional warehouse may use advanced software or a manual system, depending on the budget. |
| Scalability | Most of the managed warehouses are highly scalable i.e, they can accommodate products based on the product demand. | Traditional warehouses have limited scalability. The business needs to invest in infrastructure and staff to accommodate more products. |
Benefits Of Managed Warehousing For Businesses
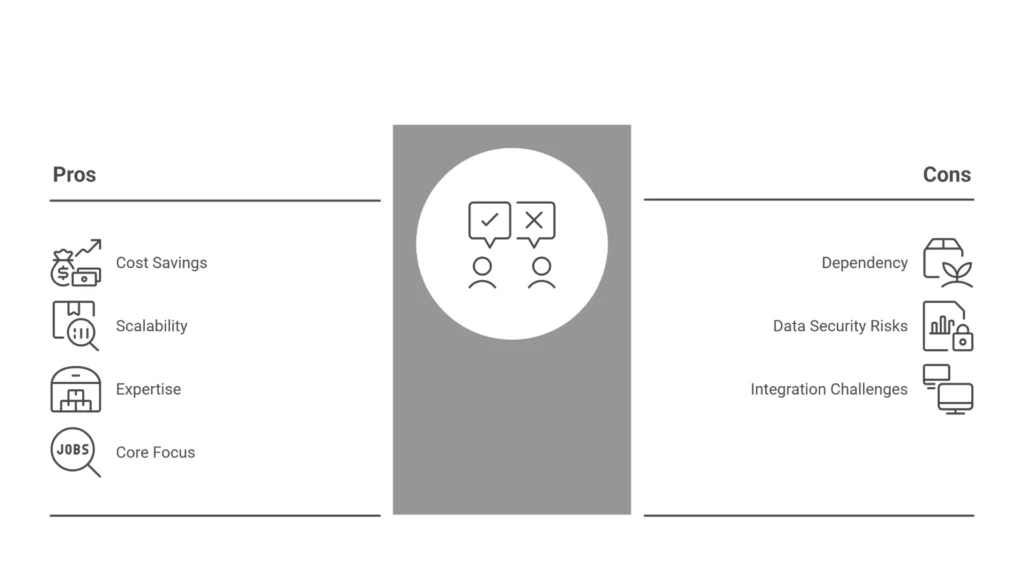
A managed warehouse has various benefits. Here is a list of them below.
1. Cost Savings
Managing inventory is crucial in supply chain management. That's why the warehouse plays a vital role in enhancing supply chain efficiency. However, building a warehouse facility requires a lot of investment. Again, the business must recruit staff, pay for utilities, and purchase heavy equipment, such as forklifts, to manage various operations. This is not possible for many small and medium-sized enterprises. These businesses can store their inventories in the managed warehouse. Companies need to pay only for the space and services they utilize.
2. Scalability
Product demand can increase during a specific season or holiday. It needs space to accommodate more products. A managed warehouse is highly scalable, which means it can adjust its space and services according to business requirements.
3. Expertise
The managed warehouse utilises advanced technology, including scan-based operations, robotics, and automation. It speeds up order fulfillment, reduces errors, and enhances customer satisfaction.
4. Focus On Core Business
A managed warehouse enables a business to focus on core activities, such as product development and exploring new markets.
Challenges & Risks Of Managed Warehousing
Managed warehousing also comes with a few challenges. Here is a list of them below.
1. Dependency On Third-party Provider
When a business outsources supply chain activities, such as warehousing, to a third-party provider, i.e., managed warehousing, it must heavily depend on its infrastructure and technology. Any delay in order fulfillment can negatively affect customers and decrease brand reputation.
2. Data Security Risks
Managed warehouses are usually equipped with advanced technology. Multiple businesses use such technology. So, there are higher chances of data breaches or cyberattacks, which can leak sensitive business information or client databases.
3. Integration Challenges
Integration with the warehouse management system, as well as the business ERP or order management tools, can be challenging. Improper integration can lead to stock problems.
Is Managed Warehouse The Right Choice for Your Business?
A managed warehouse is beneficial if you have limited upfront investment and experience fluctuating product demand in the market.
However, companies with stable product demand or a need for highly customised products should have their own private warehouse for storing inventories.
Final Words
Warehousing is a designated facility that allows a business to store products till a customer orders them. There are various types of warehouses, like private warehouses, public warehouses, and managed warehouses. A third-party logistics company manages all the order fulfillment operations on behalf of a business in a managed warehouse. It lets a business focus on essential things like product design and development. However, it has certain limitations, such as the company having limited control over the warehousing operations.




